Just what are we talking about?
- Tim Bond
- Dec 1, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: Mar 26
Glossary of Electric Vehicle Terms for Beginners
As more and more ICE (sorry, Internal Combustion Engine) drivers turn to electric vehicles, the more they come in contact with terms and phrases they may not have heard before. As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, understanding the terminology associated with them is essential for new buyers and enthusiasts. Here’s a detailed glossary of key terms to help you navigate the world of electric vehicles.
1. Electric Vehicle (EV)
An electric vehicle is a car that runs entirely on electricity instead of traditional fuels like gasoline or diesel. EVs are powered by electric motors and use large battery packs to store energy. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional vehicles.
2. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A BEV is a type of electric vehicle that operates solely on electricity stored in its batteries. Unlike hybrids, BEVs have no internal combustion engine, which means they produce no tailpipe emissions and rely completely on electric power. Examples include the Tesla Model 3 and the Nissan Leaf.
3. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
A PHEV combines an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and can be plugged in to recharge its battery. This allows it to operate on electricity alone for a limited range (typically 20-50 km) before switching to gasoline. PHEVs offer the flexibility of electric driving with the backup of a gasoline engine, making them suitable for longer trips without range anxiety.

4. Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
An HEV uses both an internal combustion engine and an electric motor but cannot be plugged in to recharge. Instead, it charges its battery through regenerative braking and by using the engine itself. HEVs are designed primarily for efficiency, optimizing fuel consumption without relying solely on electric power. Popular examples include the Toyota Prius and Honda Insight.
5. Range
Range refers to the maximum distance an EV can travel on a single charge of its battery. For instance, if an EV has a range of 400 km, it can drive that distance before needing to recharge. Range can vary based on driving conditions, terrain, and how aggressively the vehicle is driven.
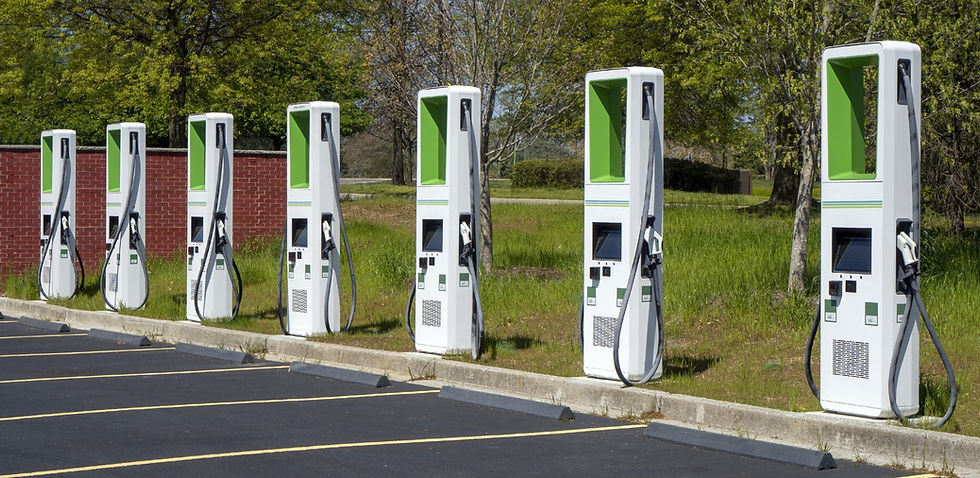

6. Charging Station
A charging station is a location where EVs can be recharged. Charging stations come in various forms, including home chargers installed in garages, public chargers located in parking lots or along highways, and fast chargers designed for quick top-ups during long trips.
7. Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging uses a standard household outlet (120V) to charge an EV. This method is the slowest charging option, typically providing about 5-10 km of range per hour of charging time. It’s suitable for overnight charging at home but may not meet the needs of daily drivers who require quicker turnaround times.
8. Level 2 Charging
Level 2 charging uses a dedicated charging unit (240V) and is commonly found in public charging stations as well as home installations. This method provides a faster charge, usually adding about 20-40 km of range per hour, making it more convenient for regular use or during short stops.
9. DC Fast Charging
DC fast charging provides rapid charging using direct current (DC). This technology allows EVs to charge to about 80% in as little as 30 minutes at compatible stations, making it ideal for long-distance travel where quick recharging is essential. DC fast chargers are typically found along major highways and in urban areas.

10. Regenerative Braking
Regenerative braking is a technology that allows an EV to recover energy while slowing down or braking. Instead of wasting energy as heat during braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into stored energy in the battery. This process helps extend the vehicle's range by reusing energy that would otherwise be lost.
11. Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
A kilowatt-hour is a unit of energy used to measure battery capacity and electricity consumption. For example, if an EV has a 60 kWh battery, it can theoretically provide enough energy to power a device that uses one kilowatt for one hour or run for approximately 200-300 km depending on efficiency.
12. Charging Network
A charging network refers to the system of public charging stations available for EV owners to recharge their vehicles on the go. Major networks in Australia include ChargeFox and Evie Networks, which provide access to fast chargers across urban areas and highways, facilitating long-distance travel for EV users.
Understanding these terms will help you navigate the growing world of electric vehicles more confidently. As EV technology continues to evolve and expand, familiarizing yourself with this vocabulary will enhance your knowledge and make your transition to electric driving smoother and more enjoyable.
Whether you're considering purchasing an EV or simply want to learn more, this glossary serves as a helpful starting point for your journey into electric mobility.



Comentários